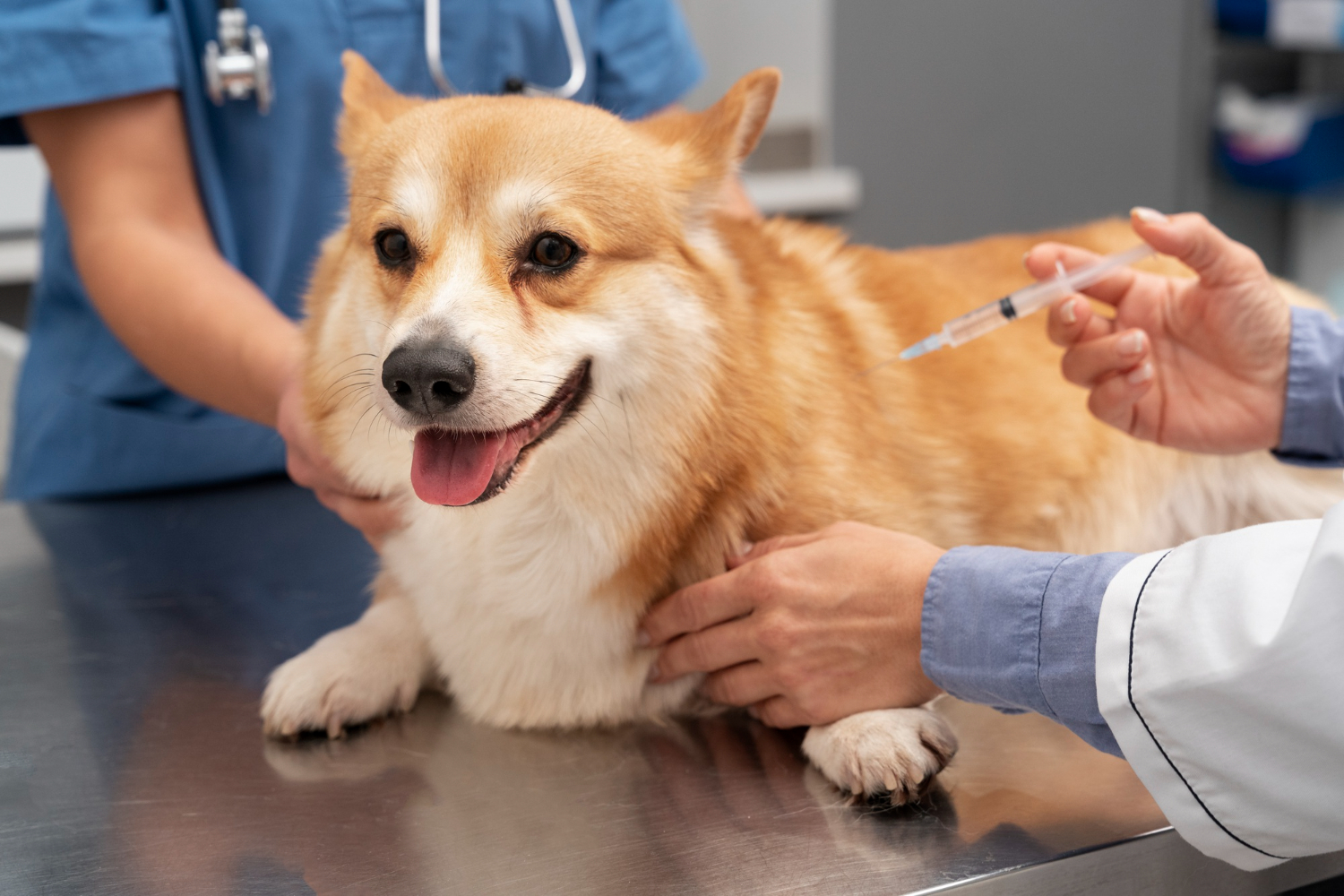
Ensuring the well-being of our furry companions involves various aspects of pet care, and one integral component is vaccinations. These crucial interventions play a pivotal role in safeguarding the health of our pets, particularly dogs. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the importance of pet vaccinations, the recommended schedules, and the impact on dog health. Understanding the significance of vaccinations empowers pet owners to make informed decisions, contributing to the overall well-being of their canine friends.
The Basics of Pet Vaccinations
Pet vaccinations are preventive measures designed to protect animals from potentially serious and life-threatening diseases. Vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize and defend against specific pathogens, such as viruses or bacteria. In the realm of dog health and general pet care, vaccinations are essential for averting the spread of contagious diseases.
Common Vaccines for Dogs
- Core Vaccines:
- Canine Distemper: A highly contagious and often fatal virus affecting various bodily systems.
- Canine Parvovirus: Causes severe gastrointestinal distress and can be fatal, especially in puppies.
- Canine Adenovirus (Hepatitis): Affects the liver and can lead to serious complications.
- Non-Core Vaccines:
- Bordetella bronchiseptica (Kennel Cough): Common in environments where dogs are in close proximity.
- Leptospira: Protects against bacteria causing leptospirosis, a potentially deadly disease.
Importance of Pet Vaccinations for Dog Health
- Prevention of Deadly Diseases:
- Pet vaccinations are the primary line of defense against diseases like distemper, parvovirus, and hepatitis, which can be fatal if contracted.
- Herd Immunity:
- Vaccinating a significant portion of the pet population contributes to herd immunity, protecting even unvaccinated animals.
- Public Health:
- Certain diseases, like rabies, pose a threat to public health. Vaccinating pets helps prevent the transmission of zoonotic diseases to humans.
- Cost-Effective Healthcare:
- Preventing diseases through vaccinations is often more cost-effective than treating illness, especially in severe cases.
- Long-Term Health and Well-Being:
- Regular vaccinations contribute to the overall longevity and well-being of dogs, promoting a healthier and happier life.
Vaccination Schedules
Understanding the recommended vaccination schedules is vital for responsible pet care and maintaining dog health. Veterinarians typically follow guidelines established by veterinary organizations to ensure optimal protection while minimizing the risk of over-vaccination.
- Puppy Vaccination Schedule:
- Puppies receive a series of vaccinations starting at around 6-8 weeks of age.
- Core vaccines, such as distemper, parvovirus, and adenovirus, are administered in multiple doses, usually 3-4 weeks apart.
- Non-core vaccines may be introduced based on the dog’s lifestyle and potential exposure.
- Adult Dog Vaccination Schedule:
- After the initial puppy series, adult dogs receive booster shots at regular intervals to maintain immunity.
- Core vaccines are typically administered every 1-3 years, depending on the specific vaccine and the dog’s risk factors.
- Non-core vaccines may be recommended annually or as deemed necessary.
Addressing Concerns and Myths
While pet vaccinations are crucial for dog health, there are often concerns and myths that circulate among pet owners. Addressing these issues is essential for fostering understanding and promoting responsible pet care.
- Over-Vaccination:
- Some pet owners worry about over-vaccination. However, guidelines from veterinary organizations emphasize the importance of tailoring vaccination schedules to individual dogs based on their risk factors.
- Vaccine Side Effects:
- Like any medical intervention, vaccines can have side effects. Common side effects are typically mild and short-lived, such as lethargy or mild swelling at the injection site.
- Natural Immunity:
- While some diseases may confer natural immunity after recovery, relying on natural immunity is risky. Vaccination provides a controlled and safer means of building immunity without exposing the pet to the full-blown disease.
Choosing a Veterinarian and Open Communication
Selecting a trusted veterinarian is a pivotal aspect of ensuring proper pet care, including vaccinations. Regular check-ups allow for open communication about the pet’s health, lifestyle, and any concerns the owner may have. A collaborative relationship between pet owners and veterinarians ensures that vaccination decisions align with the individual needs of the dog.
In the intricate tapestry of pet care and dog health, vaccinations stand as a cornerstone for preventing the spread of infectious diseases and promoting overall well-being. Understanding the significance of pet vaccinations, following recommended schedules, and addressing concerns contribute to responsible pet ownership.
As guardians of our canine companions, it is our responsibility to make informed decisions that prioritize the health and happiness of our pets. Regular veterinary consultations, adherence to vaccination schedules, and open communication with veterinarians form the pillars of a comprehensive approach to dog health. By embracing the importance of vaccinations, we pave the way for a future where our beloved dogs can lead long, vibrant lives as cherished members of our families.
Image by Freepik